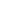MOOSstart

Collaborative project "Yield increase and upscaling of seed production and application as an initial step for the cultivation of renewable peat moss biomass in paludiculture".
MOOSstart addresses three challenges of our time and aims to contribute to achieving the goals of the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement: The aims are to reduce CO2 emissions from drained peat soils to as close to zero as possible through rewetting, to end the use of fossil peat in gardening and at the same time to ensure alternatives for land use and commercial horticulture.
The cultivation of peat moss in paludiculture offers the unique opportunity to produce high-quality renewable substrate raw materials for commercial horticulture on rewetted and degraded raised bogs - with benefits for climate and biodiversity. This has been demonstrated by the predecessor project MOOSzucht and the research projects MOOSGRÜN, MOOSWEIT and OptiMOOS.
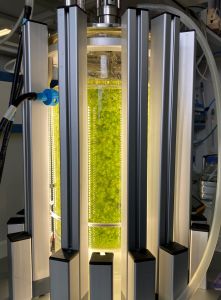
In order to scale up peat moss paludiculture, MOOSstart focuses on the first part of the production chain: the fabrication of large quantities of seeds for the establishment of new areas. In the previous MOOSzucht project, it was possible to axenically propagate vegetative starting material in a photobioreactor. The focus of MOOSstart is to further develop this process and construct a low-cost bioreactor so that it can be used on a larger scale, more cost-effectively and as decentrally as possible. A test run is also planned for the first low-cost bioreactor, which is to be set up with a potential user. For the starter material produced, MOOSstart is investigating the adaptation and development of suitable technology for sowing on rewetted raised bog soils. MOOSstart is also working on increasing crop yields - a decisive factor for the profitability of peat moss paludiculture.
The project results are intended to contribute to the transformation towards climate-neutral peatland use and substrate management and thus strengthen Germany's pioneering role in peat moss paludiculture and the sustainable production of renewable substrate raw materials.
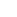
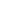
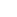
Cultivation of peat mosses and propagation in the photobioreactor (Photos: N. Körner)
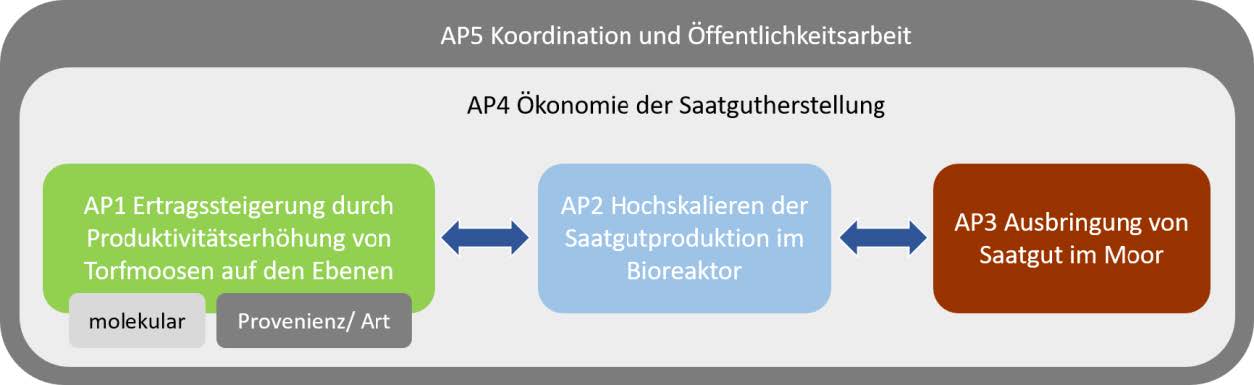
Main areas of work
The joint project MOOSstart includes:
- Increasing the productivity of peat mosses at the molecular (UF and HSA) and provenance/species level (UG, orders)
- Development of a low-cost bioreactor for upscaling the mass propagation of vegetative peat moss starting material (HSA) and test run with a potential user (NIRA)
- Economy of starting material production in the low-cost bioreactor (HSA)
- Development of an adapted technique for the application of peat moss starting material produced in the low-cost bioreactor (NIRA)
- Coordination and public relations (UG)
Joint network partners
- University of Greifswald, Institute of Botany and Landscape Ecology (UG), partner in the Greifswald Mire Center (GMC), peatland research group
- University of Freiburg (UF), Institute of Biology II Working Group: Plant Biotechnology
- Anhalt University of Applied Sciences, Department of Applied Biosciences and Process Engineering (HSA)
- Lower Saxony Turf Cultures, NIRA GmbH & Co. KG (NIRA)